Rail transport in Ireland
| Ireland | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 An Iarnród Éireann 22000 Class DMU at Drogheda MacBride station | |||||
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | Iarnród Éireann (Republic of Ireland) NI Railways (Northern Ireland) | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | 50 million (Republic of Ireland, 2019)[1] 15 million (Northern Ireland, 2017)[2] | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 2,733 km (1,698 mi) | ||||
| Electrified | 53 km (33 mi) | ||||
| Freight only | 362 km (225 mi) | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main | 1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in) | ||||
| Electrification | |||||
| 1500 V DC | DART in Dublin | ||||
| Features | |||||
| Longest tunnel | Cork railway tunnel | ||||
| Longest bridge | Barrow Bridge | ||||
| No. stations | 147 | ||||
| |||||
Rail transport in Ireland (InterCity, commuter and freight) is provided by Iarnród Éireann in the Republic of Ireland and by Northern Ireland Railways in Northern Ireland.
Most routes in the Republic radiate from Dublin. Northern Ireland has suburban routes from Belfast and two main InterCity lines, to Derry and cross-border to Dublin.
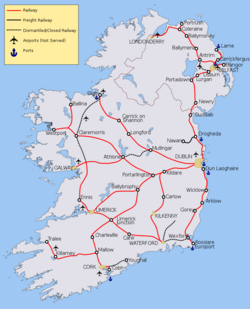
The accompanying map of the current railway network shows lines that are fully operational (in red), carrying freight only traffic (in black) and with dotted black lines those which have been "mothballed" (i.e. closed to traffic but potentially easy to re-open). Some airports are indicated but none are rail-connected, although Kerry Airport and Belfast City Airport are within walking distance of a railway station. Both the City of Derry Airport and Belfast International (Aldergrove) are near railway lines but not connected. Ports are marked, although few remain rail-connected. Dublin Port, Larne Harbour, Belview Port and Rosslare Europort are ports that are still connected.
Ireland's only light rail service, named Luas, is in Dublin. No metro lines currently exist in Ireland, but there is a planned MetroLink line which would serve Dublin.
History
[edit]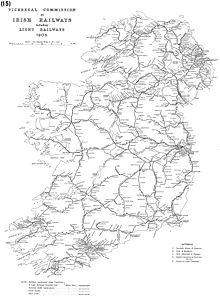
The first railway in Ireland opened in 1834. At its peak in 1920, Ireland had 5,600 km (3,480 mi) of railway; now only about half of this remains. A large area around the border has no rail service.
Ireland's first light rail line was opened on 30 June 2004.
Rolling stock
[edit]Locomotives
[edit]Diesel traction is the sole form of motive power in both the IÉ and NIR networks, apart from the electrified Howth/Malahide-Greystones (DART) suburban route in Dublin. Apart from prototypes and a small number of shunting locomotives, the first major dieselisation programme in CIÉ commenced in the early 1950s with orders for 94 locomotives of two sizes (A and C classes) from Metropolitan-Vickers which were delivered from 1955, with a further twelve (B class) locomotives from Sulzer in the late 1950s. Following poor reliability experience with the first generation diesel locomotives, in the 1960s a second dieselisation programme was undertaken with the introduction of sixty-four locomotives in three classes (121, 141 and 181) built by General Motors, of the United States. This programme, together with line closures, enabled CIÉ to re-eliminate steam traction in 1963, having previously done so on the CIÉ network prior to taking over its share of the Great Northern Railway. In parallel, NIR acquired three locomotives from Hunslet, of England, for Dublin-Belfast services. The Metropolitan-Vickers locomotives were re-engined by CIÉ in the early 1970s with General Motors engines.
The third generation of diesel traction in Ireland was the acquisition of eighteen locomotives from General Motors of 2475 h.p. output, designated the 071 class, in 1976. This marked a significant improvement in the traction power available to CIÉ and enabled the acceleration of express passenger services. NIR subsequently purchased three similar locomotives for Dublin-Belfast services, which was the first alignment of traction policies by CIÉ and NIR.
A fourth generation of diesels took the form of thirty-four locomotives, again from General Motors, which arrived in the early 1990s. This was a joint order by IÉ and NIR, with thirty-two locomotives for the former and two for the latter. They were again supplied by General Motors Electro-Motive Division. IÉ designated their locomotives the GM 201 class; numbered 201 to 234 (the NIR locomotives were later prefixed with an 8). These locomotives are the most powerful diesels to run in Ireland, and are of 3200 horsepower (2.5 MW), which enabled further acceleration of express services. The NIR locomotives, although shipped in NIR livery, were repainted in 'Enterprise' livery, as were six of the IÉ locomotives.
The 071 class are now used on freight services. NIR's three similar locomotives are numbered 111, 112 and 113. There is seldom more than one of these serviceable at a time.
Multiple units
[edit]NIR and IÉ both run suburban services using diesel multiple units (DMUs) – these are termed railcars in Ireland (see rail terminology).
Railcars currently operating in Ireland
[edit]| Class | Image | Type | Top speed | Number | Routes operated | Built | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||
| 2600 Class | 
|
Diesel multiple unit | 70 | 110 | 8 |
|
1993 |
| 2800 Class | 
|
75 | 120 | 8 |
|
2000 | |
| 3000 Class | 
|
90 | 145 | 23 |
|
2003–2005 | |
| 4000 Class | 
|
90 | 145 | 20 |
|
2010–2021 | |
| 22000 Class | 
|
100 | 160 |
|
|
2007–2012 | |
| 29000 Class | 
|
75 | 120 | 29 |
|
2002–2005 | |
| a Only 6 Class 3000 units are equipped with CAWS, which allows them to operate in the Republic of Ireland. | |||||||
IÉ DMUs operate all InterCity services apart from Dublin to Cork and some Dublin to Belfast services (one service per week from Dublin Connolly to Belfast and back is Railcar).
There are 234 22000 Class carriages in total, being formed into the following sets:
- Ten 5-car sets – Each set includes a 1st Class Carriage and a Dining Carriage. They are used on key InterCity services between Dublin and Limerick, Galway, Waterford, Westport and Tralee.
- Twenty-five 4-car sets – These mostly operate on their own or with a 3-car unit. They serve lesser-used InterCity services and most Dublin to Sligo and Rosslare services.
- Twenty-eight 3-car sets – These mostly operate in pairs. They serve lesser-used InterCity services and many Dublin Commuter services.
Features of the InterCity Railcar fleet include:
- Automatic PA and information display systems
- Electronic seat reservation displays for web bookings
- Fully air-conditioned
- Internal CCTV system
- Sleek carriage design
- Advanced safety features throughout
The primary DMU classes in operation include the 22000, 29000, 2800, 2600, 3000, and 4000 series.
Introduced between 2002 and 2005, the 29000 Class consists of 29 four-car sets built by CAF. These units primarily operate on suburban routes in the Greater Dublin area, offering a seating capacity of 185 per set.
The 2800 Class includes 10 two-car sets constructed by Tokyu Car Corporation in 2000. Initially deployed on regional services, these DMUs have been reassigned to various routes based on operational requirements, each set providing seating for 85 passengers.
Built by Tokyu Car Corporation and introduced in 1993, the 2600 Class comprises 17 two-car sets. These units were the first modern DMUs purchased for the network and were initially used on suburban services.
The 3000 Class DMUs, manufactured by CAF, were introduced between 2004 and 2005. This fleet consists of 23 three-car sets, each with a seating capacity of approximately 212 passengers.
The 4000 Class DMUs, also built by CAF, entered service between 2011 and 2012. The fleet comprises 20 sets, configured into both three-car and six-car formations. Each three-car set offers seating for 216 passengers, while six-car sets accommodate up to 442 passengers. These units feature enhanced seating capacity and fuel economy compared to earlier models. In 2018, an additional 21 vehicles were ordered to extend train lengths, facilitating longer formations and increased capacity
Coaching stock
[edit]Mark 4 carriages
[edit]Iarnród Éireann's flagship InterCity fleet are the Mark 4.

Built by CAF of Spain in 2004–2005 they are formed into 8-car push-pull sets. Each set contains (in order):
- GM 201 class locomotive
- 5 Standard class carriages
- 1 restaurant carriage
- 1 'Citygold' (first class) carriage
- Generator Control Car
The Mark 4 trains have blue tinted windows, which help to create a cool journey for the passenger, electronic route maps showing train progress, electronic seat reservation displays and power points for laptops, or recharging tablets, MP3 players or mobile phones. Citygold customers on this fleet have the added features of adjustable seating, greater room and comfort and in-seat audio entertainment. They are used exclusively on the Dublin to Cork route; operating an hourly service each way.
The Mark 4 trains are capable of speeds of up to 125 mph (201 km/h), but are limited to a maximum speed of 100 mph (160 km/h), due to the lines they run on and the locomotives that pull them.
Enterprise services
[edit]The Dublin to Belfast 'Enterprise' service is operated jointly by IÉ and NIR with rolling stock from De Dietrich, commissioned in 1997. Four Mark 3 Generator vans were introduced in September 2012. Until then, 201 Class locomotives were required to supply head-end power (HEP) for heating and lighting. Since late 2024, with a timetable change increasing services up to every hour on Enterprise,[citation needed] Translink Class 4000 and Irish Rail 22000 Class trains have also began running on the Enterprise.[citation needed]

Previous stock
[edit]NIR also had a number of refurbished Class 488 carriages acquired from the Gatwick Express service and converted to run on the Irish 1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in) gauge. These were generally referred to as 'the Gatwicks'.[by whom?] They were in use from 2001 until June 2009.
Passenger services
[edit]
Below is a list of all passenger routes on the island of Ireland. Please note the following when examining routes:
- Services below usually, but not necessarily always, involve a change of trains. Changing points are shown in bold type.
- Services at different times of day will serve a different subset of the stations shown below. The "stations served" lists all possible stops for any train on a given route. As an example, some services to Limerick do not involve a change at Limerick Junction, and some services to Cork may stop at Limerick Junction, Charleville and Mallow only.
Republic of Ireland InterCity routes
[edit]Dublin to Cork
[edit]Stations served on this line are
- Dublin Heuston
- Portlaoise
- Ballybrophy
- Templemore
- Thurles
- Limerick Junction
- Charleville
- Mallow
- Cork Kent
This was known as the 'Premier Line' of the Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR), being one of the longest routes in the country (266 km or 165 miles), built to a high standard and connecting to Galway, Limerick, Waterford and County Kerry, as well as to Cork. These other destinations all have their own services, although connections are offered to/from the Cork service at Limerick Junction (for Limerick) and Mallow (for Kerry). As of 2019 the line is receiving a major upgrade focusing this year between Newbridge and Ballybrophy.[citation needed] There are possessions of most sections of the line every night to carry out relaying. There are also disruptions and cancellations on most weekends.[citation needed] All relaying is using a much heavier rail to give a much smoother ride on trains.[citation needed] The new track at 60 kg, is the same that is used on the TGV in France. As the upgrading continues there are speed restrictions which are affecting punctuality of trains.[citation needed] A new platform is under construction at Limerick Junction on the down line which will reduce conflicts and reduce journey times by 3–5 minutes.[citation needed] A fourth track is planned between Park West-Cherry Orchard and Heuston which is also intended to further reduce journey times.[citation needed] As of 2019, 13 out of 29 services on the route daily are delivered in 2 hours 30 mins or under.[citation needed] 11 trains operate the service in between 2 hours 30 mins and 2 hours 35 mins, with all services 2 hours 40 mins or less. An early morning express service from Cork to Dublin makes the non-stop journey in 2 hours 15 mins.[3][failed verification]
Dublin to Limerick
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Heuston
- Sallins and Naas
- Newbridge
- Kildare
- Monasterevin
- Portarlington
- Portlaoise
- Ballybrophy
- Templemore
- Thurles
- Limerick Junction
- Limerick Colbert
This service follows the Cork route as far as Limerick Junction. Limerick services leave the main line via a direct curve built in 1967, onto part of the former Waterford and Limerick Railway (W&LR). The former two hourly timetable operated by 22000 Class railcars was cut back in November 2009 when the number of direct trains was reduced to three from Dublin to Limerick and four from Limerick to Dublin. On Sunday there are 6 trains in each direction. The remaining Dublin-Limerick-Ennis services involve a change at 'Limerick Junction' from a Dublin-Cork or Dublin-Tralee service onto a local train for the remaining 30 minutes of the journey.
Dublin to Galway
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Heuston
- Sallins and Naas (peak times only)
- Newbridge
- Kildare
- Monasterevin
- Portarlington
- Tullamore
- Clara
- Athlone
- Ballinasloe
- Woodlawn
- Attymon
- Athenry
- Oranmore
- Galway Ceannt
The present route, built by the GS&WR in competition with the MGWR, leaves the Cork main line just after Portarlington. The River Shannon is crossed at Athlone. Athenry, the second last station before Galway, became a junction once again in 2010 with the reopening of the line to Limerick and would do so again if the planned reopening of the line to Tuam proceeds in accordance with Transport 21. In February 2011 planning permission was obtained for a station at Oranmore and opened 28 July 2013. All services are operated by 22000 Class railcars.
As of 2019, journey times range between 2 hours 11 minutes to 2 hours 37 minutes. 8 services operate in 2 hours 20 mins or less Monday to Friday. There are 9 direct trains in each direction Monday–Thursday. On Friday the 07:35 express Heuston goes to Westport instead of Galway but there is a connecting train to Galway from Athlone. For the college term there is an extra service from Galway to Dublin at 15:35.
Dublin to Tralee
[edit]
Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Heuston
- Kildare (1 train on Sunday)
- Portarlington (Sundays only)
- Portlaoise
- Thurles
- Limerick Junction
- Charleville
- Mallow
- Banteer
- Millstreet
- Rathmore
- Killarney
- Farranfore
- Tralee Casement[citation needed]
This relatively indirect route runs along what is in essence a branch line connected to the Cork–Dublin mainline at Mallow. Trains run to/from the south of Tralee. As of 2017 there were eight trains from Mallow to Tralee and nine trains the other way around. All services are operated by 22000 Class railcars, with the exception of the very early morning service from Tralee to Cork and some Sunday services (From Tralee to Cork via Mallow) which are operated by a 2-carriage 2600 Class Commuter set. There is one service a day from Dublin Heuston to Tralee in each direction Monday to Friday. On Sunday there is two trains from Heuston to Tralee and three from Tralee to Heuston. Journey times range from 3 hours 40 minutes to 3 hours 53 minutes. On this line, Farranfore railway station provides a direct connection with Kerry Airport.[citation needed]
Dublin to Waterford
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Heuston
- Hazelhatch and Celbridge
- Sallins and Naas
- Newbridge
- Kildare
- Athy
- Carlow
- Muine Bheag
- Kilkenny MacDonagh
- Thomastown
- Waterford Plunkett
Since Kilkenny is a stub station, reversal is necessary. Non Passenger trains such as the DFDS Freight train from Ballina to Waterford avoid Kilkenny by using Lavistown loop which joins both lines going into Kilkenny. Some passenger trains use the loop to reducing the journey time.[citation needed]
Dublin to Westport/Ballina
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Heuston
- Newbridge
- Kildare
- Monasterevin
- Portarlington
- Tullamore
- Clara
- Athlone
- Roscommon
- Castlerea
- Ballyhaunis
- Claremorris
- Manulla Junction (Foxford–Ballina or Castlebar–Westport)
The line is served primarily by a 22000 Class DMU on Dublin–Westport. On the Manulla Junction – Ballina section a 2800 Class diesel railcar operates. There are 3 services a day from Heuston to Westport and 5 From Westport to Heuston Monday to Thursday and on Friday the 07:35 Heuston to Galway goes to Westport and the 09:08 Athlone to Westport goes to Galway and then the 17:10 Heuston to Athlone is extended to Westport and there is 5 trains from Westport to Heuston. There is also 1 service daily from Athlone to Westport Monday to Thursday. Journey times range from 3 hours 6 minutes to 3 hours 44 minutes.[citation needed]
Dublin to Gorey/Rosslare Europort
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Connolly
- Tara Street
- Dublin Pearse
- Dún Laoghaire Mallin
- Bray Daly
- Greystones
- Kilcoole (limited service)
- Wicklow
- Rathdrum
- Arklow
- Gorey
- Enniscorthy
- Wexford O'Hanrahan
- Rosslare Strand
- Rosslare Europort
There are four end to end journeys in each direction Mondays to Fridays inclusive. There is a once-daily morning commuter service from Dundalk Clarke to Bray Daly and another from Drogheda MacBride to Bray Daly. In the evening, there is a once-daily commuter service from Dún Laoghaire Mallin to Dundalk Clarke, as well as a service from Bray to Drogheda MacBride.. On Saturdays and Sundays there are three end to end journeys each way plus a Gorey to Dundalk Commuter service. The 16:37 Dublin Connolly to Rosslare Europort Mondays to Fridays journey offers connectional opportunities into ships to Wales and France. Some peak services also stop at Lansdowne Road station as well and some services skip Kilcoole. This service has the slowest average speed at roughly 53 kilometres per hour. Services are either ICR's of 29000 commuter trains.[4][5]
A resignalling project in Dublin increases the ability of Iarnród Éireann to run 12 to 20 trains per hour in both directions through the Howth Junction to Grand Canal Dock line, which caters for Howth DARTs, Malahide DARTs, Northern Commuter trains, Belfast Enterprise services, Sligo InterCity and Maynooth Commuter services, as well as other services in the Connolly to Grand Canal Dock area.[6]
Dublin to Sligo
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Dublin Connolly
- Drumcondra
- Maynooth
- Kilcock
- Enfield
- Mullingar
- Edgeworthstown
- Longford
- Dromod
- Carrick-on-Shannon
- Boyle
- Ballymote
- Collooney
- Sligo Mac Diarmada
All services are operated by 22000 Class railcars with a service every 2 hours until 7 pm. The first Sunday service from Dublin is operated by 29000 Class railcars. This returns from Sligo at 6 pm.
Cork to Tralee
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
This is a three times daily service with two trains departing in the morning and one in the evening. The service is run by a 22000 Class.
Farranfore railway station connects with Kerry Airport.
Limerick to Waterford
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
The Limerick–Waterford route is the only true non-radial (from Dublin) route still open in Ireland that is not a branch line. The route was commenced in 1848 by the Waterford & Limerick Railway and completed in 1854.
Timetabling, as of 2019, requires passengers to change at Limerick Junction. There are two services per day, each way, with no service on Sundays or Public Holidays. Timetabled journey times vary between 2hrs35mins & 2hrs43mins.
Limerick–Ennis–Galway
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
This service started 30 March 2010 with the reopening of the Ennis–Athenry line. Direct trains now travel from Limerick to Galway with the Ennis commuter services have been subsumed into these.
All of the new stations are unstaffed. Gort has two platforms with lifts, bridges, ticket machines and a loop while Sixmilebridge, Ardrahan and Craughwell have just one platform each. In Gort the signal cabin has been restored and relocated and there is a small depot for permanent way crew. This reopening was the Phase One of the reopening of the Western Rail Corridor. It involved the relaying of 58 km of track, rebuilding bridges, installation of signalling systems, level crossing upgrades and building the stations. The journey time between Limerick and Galway is just under 2 hours and there are 5 trains each way daily.
The line has seen some growth, with the Irish Times reporting that from 2013 to 2014, "the western rail corridor saw a 72.5 per cent increase from 29,000 to 50,000 journeys through the Ennis–Athenry section of the line", which was partly attributed to the introduction of online booking and promotional fares.[7]
Republic of Ireland commuter routes
[edit]Dublin Suburban Rail
[edit]- Dublin Area Rapid Transit (DART) – Greystones to Howth/Malahide.
- Northern Commuter – Dublin Pearse to Drogheda MacBride/Dundalk Clarke
- South Eastern Commuter – Dublin Connolly to Gorey.
- South Western Commuter – Dublin Heuston/Grand Canal Dock to Hazelhatch and Celbridge/Portlaoise/Newbridge.
- Western Commuter – Dublin Pearse/Docklands to Maynooth/M3 Parkway/Longford.
Mallow to Cork
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
Cóbh to Cork
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
Midleton to Cork
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
Galway to Athenry
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
Limerick to Ennis
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
Limerick to Nenagh and Ballybrophy
[edit]
Stations served on this line are:
The line branches from the Waterford line just outside Limerick at Killonan Junction. All trains on this line connect with Dublin trains at Ballybrophy.
Current services on the line consist of two return passenger trains a day from Limerick. Following a campaign by The Nenagh Rail Partnership founded by local politicians and community representatives and assisted by the Internet news group Irish Railway News, a market research survey was funded by local Government. The market research was carried out in the summer of 2005 and showed there existed a market for improved services on the line. As a result of this study IÉ has committed to allocating additional rolling stock to the line as part of its ongoing fleet replacement programme. This line is subject to many speed restrictions due to the need to replace several old sections of track.
In October 2007, following a meeting between Iarnród Éireann management and The Nenagh Rail Partnership, it was confirmed that the new commuter service would be introduced between Nenagh and Limerick on Monday 1 September 2008. This was launched as planned on Monday 1 September 2008.
A news report in January 2012 suggested that Iarnród Éireann might seek permission from the National Transport Authority to close the line,[8] but in February 2012 an enhanced timetable for the line was published, indicating that a decision to close has been deferred pending the outcome of the service upgrade.[9][needs update]
Northern Ireland routes
[edit]Services in Northern Ireland are sparse in comparison to the Republic or other countries. A large railway network was severely curtailed in the 1950s and 1960s (in particular by the Ulster Transport Authority). Routes now include suburban services to Larne, Portadown/Newry and Bangor, as well as services to Derry. There is also a branch from Coleraine to Portrush. On Northern Ireland Railways distances are quoted in miles and metres.[10]
Belfast suburban
[edit]Three suburban routes run on 20-minute frequencies in and out of Belfast Grand Central, these routes then pass through Belfast Lanyon Place before continuing onto destinations at Bangor, Derry and Larne
Belfast to Derry
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Belfast Grand Central
- City Hospital
- Botanic
- Belfast Lanyon Place
- York Street (partial service)
- Whiteabbey (partial service)
- Mossley West
- Antrim
- Ballymena
- Cullybackey
- Ballymoney
- Coleraine
- Castlerock
- Bellarena
- Derry~Londonderry
The service to Derry has suffered from a lack of funding over recent decades.[citation needed] The existing line is not continuously welded and has speed restrictions in parts. For some time the threat of closure hung over this route but a funding package of £20 million was confirmed in December 2005.[citation needed] The same month saw the introduction of the new CAF railcars on the line and despite the fact that the service remained slower than the Derry-Belfast Ulsterbus service, the improvements saw a rise in passenger numbers to over 1 million per annum.[citation needed] However, these in 2007 when it was revealed that the £20 million earmarked had not been spent while there had been a £20 million overspend on the Belfast–Bangor line,[11] and the "Into the West"[12] rail lobby group had proposed extending the line cross border into County Donegal to Letterkenny and then on to Sligo, thus releasing EU funding.[13] Currently,[when?] the department has partly completed a plan in place for Regional Development, for relaying of the track between Derry and Coleraine by 2013, which includes a passing loop, and the introduction of two new train sets. The £86 million plan is expected to reduce the journey time between Belfast and Derry by 30 minutes and allow commuter trains to arrive in Derry before 0900 for the first time.[citation needed]
Coleraine to Portrush
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
Belfast to Larne Harbour
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Belfast Grand Central
- City Hospital
- Botanic
- Belfast Lanyon Place
- York Street
- Whiteabbey
- Jordanstown
- Greenisland
- Trooperslane
- Clipperstown
- Carrickfergus
- Downshire
- Whitehead
- Ballycarry
- Magheramorne
- Glynn
- Larne Town
- Larne Harbour
Cross-border routes
[edit]Belfast–Dublin and Dublin–Belfast
[edit]Stations served on this line are:
- Belfast Grand Central
- Lisburn (1 Train each way on a Sunday)
- Lurgan (1 Train each way on a Sunday)
- Portadown
- Newry
- Dundalk Clarke
- Drogheda MacBride
- Dublin Connolly
This cross border service, named Enterprise, is jointly owned and run by Northern Ireland Railways and IÉ. Despite having some of the most modern InterCity rolling stock on the island, it has been dogged by numerous problems. An historical problem on this route has been disruption to services caused by security alerts (devices on the line, hoax devices, threats and warnings). These continue to the present day.
The punctuality on this service remains poor for other reasons. The InterCity route, despite being mostly high quality continuous welded rail, is shared with suburban services outside both Belfast and Dublin.
A further problem was due to the locomotive and rolling stock arrangements. Unlike most other locomotive-hauled rolling stock in Ireland, generator vans were not part of the train – even the DVTs did not supply power. Thus the General Motors-built locomotives had to supply head-end power for lighting and heating throughout the train. Although many types of locomotive are well designed for this purpose, these particular locomotives had struggled under the extra strain. The wear on the locomotives and time out of service were unusually high. On at least two occasions locomotives had burst into flames while shuttling along the route. To avoid further damage, four Mark 3 Generator Vans entered service in September 2012.
The collapse of the Malahide Viaduct in late 2009 temporarily stopped all Enterprise services from Dublin to Belfast for 3 months.[14] The viaduct was repaired and the line re-opened in November 2009.[15]
Freight
[edit]The following freight services operate in Ireland :
- Timber trains from Ballina to Waterford Port (Belview)
- Timber trains from Westport to Waterford Port (Belview)
- Zinc ore from Tara Mines, Navan – Dublin Port (North Wall)
- International Warehousing and Transport chartered Liner from Ballina – Dublin Port (North Wall) (Started September 2009)[citation needed]
Rail freight in Ireland declined in the early 21st century,[citation needed] and IÉ closed its container rail freight business in July 2005, saying that the sector had accounted for 10% of its freight business, but 70% of its losses.[citation needed] Container freight levels had dropped to c.35 containers on three trains per day.[16] Yet Iarnród Éireann estimated that a minimum of eighteen 40-foot containers was needed for a commercially viable trainload. The impact of this will be about forty more lorries a day, described by Iarnród Éireann as a 'drop in the ocean' when compared to the 10,000 lorries entering Dublin Port every day.[citation needed]
Freight services no longer running include ammonia trains (from Shelton Abbey, Wicklow–Cork due to the closure of a fertiliser plant),[citation needed] nationwide bagged cement and beer keg freight,[citation needed] gypsum loads (Kingscourt–Dublin), and bulk cement (from cement factories at Platin near Drogheda and Castlemungret near Limerick to silos at Sligo, Athenry, Cabra, Cork, Waterford, Tullamore and Belfast).[citation needed]
Other losses included services carrying fertilisers, grain, tar, scrap metal, molasses and coal.[citation needed] The last bulk cement flow to operate in Ireland (Castlemungret – Waterford) ended in December 2009 along with the Kilmastulla Quarry – Castlemungret Shale traffic, despite making profits in the region of €1.3 million in 2006.[citation needed]
Remaining freight traffic is supported by an agreement with Coillte to increase timber trains from Ballina to Belview from three to four weekly.[citation needed] This may[original research?] reflect the failure of the railway to dispose of its surplus Class 201 locomotives made surplus by the retirement of the Mark 3 coach fleet.[citation needed]
Bord na Móna operates an extensive 1,930 km (1,199 mi) narrow-gauge railway. This is one of the largest industrial rail networks in Europe and is completely separate from Ireland's passenger rail system operated by Iarnród Éireann. It is used to transport peat from harvesting plots to processing plants and power stations of the Electricity Supply Board.
Rail interest groups and museums
[edit]This section reads like a directory. (May 2021) |
Ireland has a small heritage railway scene, with some substantial and long-running groups operating, while most are small affairs.[citation needed] There are a couple of railtour-operating groups, one 5 ft 3 in (1,600 mm) self-contained railway, and a few groups with short lines.
Heritage railways and bodies
[edit]Heritage bodies in Ireland include the Railway Preservation Society of Ireland which is based in Whitehead, County Antrim and also has an operational base in Dublin. It runs preserved steam trains on several main lines around Ireland. Other bodies include the Irish Traction Group, which preserves diesel locomotives including an example at Carrick-on-Suir station, four at Moyasta, and five at the DCDR.[citation needed]
Heritage railways include the:
- Connemara Railway, based at Maam Cross, County Galway, operating a temporary narrow gauge railway[17]
- Downpatrick and County Down Railway, the only self-contained full-size heritage railway in Ireland,[citation needed] running trains along its 4 miles of track in addition to its static museum.
- Fintown Railway, which runs a former County Donegal Railways Joint Committee (CDRJC) railbus along the shore of Lough Finn.
- Foyle Valley Railway in Derry, which closed in 2015 but reopened in 2016.[citation needed]
- Giant's Causeway and Bushmills Railway, a recreation of the original Giant's Causeway Tramway. Steam running ceased at the railway in 2012 with the arrival of a new-build tram.
- Listowel and Ballybunion Railway, a section of the Lartigue Monorail system, has been restored for visitors in Listowel, County Kerry
- Stradbally Woodland Railway, run by the Irish Steam Preservation Society.
- Tralee and Dingle Light Railway, in County Kerry.
- Waterford Suir Valley Railway, which runs 10 km of 3 ft gauge line between Kilmeadan and Waterford.
- West Clare Railway, with a collection of 5 ft 3 in and 3 ft stock based in the restored 'Moyasta junction' station.
Interest and record groups
[edit]The Irish Railway Record Society has a library of Irish railway documents at Heuston station and charters an annual railtour. The Modern Railway Society of Ireland promoted interest in modern-day Irish Railways and charters occasional railtours, before it was wound up in 2024.
- Irish Traction Group based at Carrick-on-Suir.
- Railway Preservation Society of Ireland based at Whitehead.
Museums and historical displays
[edit]There are a number of museums, most concerned with the 3 ft (914 mm) gauge, and restored railway stations around Ireland:
- Belturbet Railway Station, County Cavan, which is restored as a museum and has several items of rolling stock.[18]
- Castlerea Railway Museum, formerly Hell's Kitchen Railway Museum, in County Roscommon.
- Cavan and Leitrim Railway, which has 0.4 km of 3 ft gauge track and a small transport museum, located next door to Iarnród Éireann's Dromod railway station.
- Clonakilty Model Railway Village, County Cork, which has a Ruston diesel and two Park Royal carriages.[19][failed verification]
- Donegal Railway Heritage Centre, a museum dedicated to the County Donegal Railways Joint Committee housed in the former Donegal railway station.
- National Transport Museum of Ireland, mostly holding wheeled road vehicles but also with trams.[20]
- Ulster Folk and Transport Museum, a major museum which contains various railway and tramway vehicles of numerous gauges from across Ireland.
Former heritage railways and interest groups
[edit]- Clonmacnoise and West Offaly Railway, which closed in 2008.
- Shane's Castle Railway, County Antrim, which ran from 1971 to 1994/5, and was partly reused at the Giant's Causeway.
- Tralee and Blennerville Railway, which closed in 2006, and again in 2013, though the line still exists.[citation needed]
Planned and potential developments
[edit]Routes
[edit]All Island Strategic Rail Review
[edit]A public consultation for a cross-border review of the inter-city railway network was launched jointly by the Irish Minister for Transport and Northern Irish Minister for Infrastructure in November 2021,[21] with over 8,000 responses to the consultation. A draft report of the Rail Review was published on 25 July 2023.[22] The review recommended the reopening of many lines, and the creation of new lines, particularly in the northwest. It also recommended doubling and electrifying numerous stretches of track, and the creation of quadruple track and alternative routes to separate intercity from suburban services close to Dublin and Belfast. The review envisages the reopening of an alternative route from Belfast to Derry via the old “Derry Road”, as well as the Portadown to Mullingar line in the medium term.[23]
Western Rail Corridor
[edit]The first stage of the reopening of the Western Rail Corridor, between Ennis and Athenry, was completed in 2009. The section between Athenry and Claremorris is recommended to be opened under the All Island Strategic Rail Review, and has been proposed by the Government as part of the Trans-European Transport Network.[24] The section between Claremorris and Collooney was not included under the All-Island Strategic Rail Review.[22]
Dublin-Navan railway line
[edit]Phase One of the Dublin–Navan railway line was completed by Iarnród Éireann in September 2010, with Dublin's Western Commuter services travelling as far as Dunboyne and the M3 Parkway railway station. Phase Two of the line, connecting M3 Parkway to Navan via Dunshaughlin and Kilmessan, was deferred following the Post-2008 Irish economic downturn.[25] The status of this proposal was downgraded from “implementation” to “review” in August 2019.[26] Construction of line was included under the Transport Strategy for the Greater Dublin Area, 2022-2042.[27]
Waterford to Rosslare (closed)
[edit]Prior to 2010, there was a single service each way from Waterford to Rosslare stretch, operated by 2700 Class railcars taking just over 1 hour. The service closed for passenger services on 18 September 2010. The reopening of the line is recommended to be opened under the All Island Strategic Rail Review,[22] and has been proposed by the Government as part of the Trans-European Transport Network.[28]
DART and DART Underground
[edit]A proposed tunnel, connecting Heuston Station and Pearse Station and onwards to the Northern Commuter line, referred to as the DART Underground, is not planned to see any development until sometime "after 2042",[29][30] but is recommended as a long-term intervention under the All-Island Strategic Rail Review.[22]
Foynes Port
[edit]The Shannon Foynes Port Company has been seeking reinstatement of the Limerick to Foynes Railway Line, which last operated in 2000,[31] as part of their expansion plans. The route is under reconstruction and is due for reopening for freight in early 2024.[32] Passenger services on the route are envisaged under the All-Island Strategic Rail Review.[22]
Dublin Metro
[edit]MetroLink is proposed to run from a stop, Estuary, near Swords north of Dublin to the Beechwood Luas stop south of the city centre, via Dublin Airport and St. Stephen's Green. Its route proposes mainly elevated tracks in the greater Swords area, with a tunnel running from north of Dublin Airport to Charlemont. As of July 2022, the project was proposed to begin construction in 2025 and that, "all going well" it could be in operation by 2035.[33]
Luas
[edit]There have been, at various points, plans or proposals to extend Luas to Swords, Dublin Airport, Lucan, Bray, and Old Fassaroe.
There have also been proposals to create a Luas-style system in Cork City. These include plans by Cork City Council, published within the Cork Metropolitan Area Transport Strategy document in 2019.[34]
Northern Ireland Railways
[edit]The potential to reopen a number of railway lines in Northern Ireland has included speculation on such lines as the line between Antrim and Castledawson.[35][36]
The reopening of the third line between Belfast Grand Central and Adelaide is suggested.[37]
In July 2020, during a North/South Ministerial Council meeting, it was proposed to undertake a feasibility study on a possible high-speed line between Belfast and Cork via Dublin.[38]
Station changes
[edit]In February 2018 the Irish Independent reported that the National Transport Authority favoured building four new DART stations, three linked to a new DART operation from Heuston, including near Cross Guns Bridge in Cabra, within Glasnevin, and at a Docklands location, along with a new station north of Bray, at Woodbrook.[39] Calls to open or reopen stations on existing lines have been floated over the years, including Kishoge railway station, which was structurally completed in 2009 but only opened in August 2024.[40]
In Northern Ireland, Translink have opened new transport hubs in both Belfast (2024) called Belfast Grand Central Station[41][42] and Derry (2021) called the Northwest Transport Hub[43].
Rolling stock
[edit]In 2017, increasing demand led Iarnród Éireann to issue tenders for the refurbishment of 10 2700 class sets, which had been held in storage for 6 years with the intention of planned use around Limerick from early 2019. The displaced trains are intended for use in the Greater Dublin Area.[44]
As of early 2018, Iarnród Éireann announced plans to procure new DART trains capable of operating on both diesel and electric power. In 2021, supported by the National Transport Authority, Iarnród Éireann partnered with Alstom to develop new electric and battery-electric trains, which are scheduled to enter service in 2026.[45][46]
As of 2018, NI Railways had plans to invest in a third wave of new trains to meet growing demand.[47][needs update]
As of 2018, a campaign was underway to preserve four 80 Class vehicles at the Downpatrick and County Down Railway, with hopes of bringing them to the heritage railway by the end of 2018.[48] Also in 2018, one of the two Cavan and Leitrim Railway steam locomotives, No. 3 ''Lady Edith'', was proposed to be repatriated by the West Clare Railway (from the New Jersey Museum of Transportation).[49][needs update]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Railway passenger transport statistics" (PDF). Europa EU. 8 December 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 January 2021. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ "40% increase in rail passengers on Derry line". Derry Journal. 25 September 2018. Archived from the original on 25 April 2019. Retrieved 25 April 2019.
- ^ "New Rail Timetable for 2013– Iarnród Éireann". Irishrail.ie. 15 January 2013. Archived from the original on 30 January 2013. Retrieved 31 January 2013.
- ^ "Rosslare Europort - Dublin - Valid from 14.10.2024 until further notice" (PDF). irishrail.ie. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ "DART/Commuter Timetable" (PDF). irishrail.ie. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ "Investment in Iarnród Éireann". irishrail.ie. 31 January 2015. Archived from the original on 17 December 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- ^ O'Brien, Tim. "Iarnród Éireann passenger numbers up by 1 million". The Irish Times. Archived from the original on 11 February 2020. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ Seán McCárthaigh (2 January 2012). "Iarnród Éireann may close rail service amid falling demand". Examiner.ie. Archived from the original on 6 June 2012. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Nenagh, Limerick and Commuter service improvements – REVISED SCHEDULE, FROM 20TH MARCH – Iarnród Éireann". Irishrail.ie. 16 March 2012. Archived from the original on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Rail Accident Report - Derailment at Trooperslane near Carrickfergus, Northern Ireland - 23 April 2006" (PDF). raib.ie. Rail Accident Investigation Branch. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 April 2009. Retrieved 31 May 2021.
- ^ "Belfast-Bangor line". BBC News. 22 March 2007. Archived from the original on 23 October 2007. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Into the West". Intothewestrail.com. Retrieved 24 August 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "S . E . A . - Rail group seek EU funding for NW rail network". 9 August 2007. Archived from the original on 9 August 2007.
- ^ "Bridge on Dublin-Belfast Line Collapses". Raidió Teilifís Éireann. 21 August 2009. Archived from the original on 17 September 2009. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Dublin-Belfast Rail ReOpens". Raidió Teilifís Éireann. 16 November 2009. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Historical debates - Dáil Éireann - Volume 610 - 24 November, 2005 - Other Questions - Rail Services". Historical-debates.oireachtas.ie. Archived from the original on 4 February 2012. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Connemara Railway". Archived from the original on 25 June 2023. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Visit Belturbet Heritage Railway Museum with Discover Ireland". Archived from the original on 13 July 2023. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- ^ "Home - West Cork Model Railway Village".
- ^ "Howth Tram Restored". RTÉ Archives. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "All Island Strategic Rail Review". www.gov.ie. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d e "PDF.js viewer" (PDF). www.gov.ie. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 July 2023. Retrieved 25 July 2023.
- ^ "All-Island Strategic Rail Review makes 30 proposals to develop railways in Ireland". Railway Gazette International. 26 July 2023. Retrieved 21 April 2024.
- ^ "Boost for Mayo as rail line gains approval for EU funding consideration". The Connacht Telegraph. Archived from the original on 29 December 2023. Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ^ "Navan Railway Line". Iarnród Éireann - Irish Rail. Irish Rail. 31 January 2015. Archived from the original on 16 April 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- ^ "Planning minister asks that Navan Rail line priority be downgraded". Meath Chronicle. 26 August 2019. Archived from the original on 10 October 2019. Retrieved 10 October 2019.
- ^ Transport Strategy for the Greater Dublin Area, 2022-2042 (Report). National Transportation Authority. 24 January 2023. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ "Rosslare-Waterford railway line to feature in ambitious EU plan". The Irish Independent. Archived from the original on 29 December 2023. Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ^ Kilraine, John (9 November 2021). "MetroLink postponed for ten years - NTA draft strategy". rte.ie. RTÉ News. Archived from the original on 9 November 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2021.
- ^ "'We won't let go': Irish Rail is convinced the long-delayed Dart Underground will go ahead". TheJournal. 21 September 2017. Archived from the original on 28 March 2019. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- ^ "Fears over closure of Foynes rail link are allayed". The Irish Times. Archived from the original on 24 September 2021. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- ^ "Strides made in reopening Foynes to Limerick rail line for freight". Limerick Leader. Archived from the original on 29 December 2023. Retrieved 29 December 2023.
- ^ "Long-delayed Dublin Metrolink to cost €9.5bn with first trains running by 2034". independent. 4 July 2022. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ "Take the opportunity to get a look at Draft Transport Plan for Cork". Irish Independent. 1 June 2019. Archived from the original on 8 June 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ Barrow, Keith. "New lines proposed in Northern Ireland rail plan". Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ "New lines proposed in Northern Ireland rail plan". railjournal.com. 3 May 2014. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 3 May 2015.
- ^ "Third track at Adelaide - a Freedom of Information request to Northern Ireland Transport Holding Company". WhatDoTheyKnow. 21 October 2024. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ Finn, Christina (31 July 2020). "Irish and NI governments to examine the possibility of a high-speed Belfast-Dublin-Cork rail line". TheJournal.ie. Archived from the original on 2 August 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- ^ "New Dart plan backs away from underground route". The Irish Independent. Archived from the original on 9 April 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ "West Dublin train station opens 15 years after being built". rte.ie. 26 August 2024.
- ^ "Translink". www.translink.co.uk. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ "The Hub". Archived from the original on 25 July 2021. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ "North West Hub". www.translink.co.uk. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ "Iarnród Éireann to refurbish 28 carriages after six years out of service". Irish Examiner. 26 July 2018. Archived from the original on 9 September 2018. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ "DART+ DART+ Fleet". www.dartplus.ie. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ Barrow, Keith. "Irish Rail plans bi-mode train order for Dart expansion". Archived from the original on 4 April 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ "NI Railways 50th Anniversary – Translink". translink.co.uk. Translink. Archived from the original on 9 April 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ "Save an 80 class! | Downpatrick & County Down Railway". www.downrail.co.uk. Archived from the original on 8 April 2018. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ "PressReader - Steam Railway (UK): 2017-04-21 - US TAXMAN WANTS a CUT OF LADY EDIth's REPATRIATION". Archived from the original on 16 August 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2018 – via PressReader.
Further reading
[edit]- Baker, Michael H. C. (2022). Irish Railways: The Last 60 Years. World Railways Series, Vol 4. Stamford, Lincs, UK: Key Publishing. ISBN 9781802821642. Archived from the original on 15 April 2023. Retrieved 15 April 2023.
- Pritchard, R. N. (2020). Irish Railways: Locomotives, Multiple Units & Trams. European Handbook, No. 7 (4th ed.). Sheffield: Platform 5 Publishing. ISBN 9781909431461. Archived from the original on 6 May 2023. Retrieved 15 April 2023.
External links
[edit]- Website of Iarnrod Éireann (Irish Rail)
- Website of Northern Ireland Railways
- Railway Procurement Agency
- Platform For Change (Dublin Transportation Office)
- Strategic Rail Review 2003 (Department of Transport)
- Rail Users Ireland – Ireland's National Rail User organisation
- Eiretrains – Irish Railways Past & Present